The Immune System and Psoriasis
There is still no clear explanation for the link between the immune system and psoriasus. It is believed that genes play a role in the development of psoriasis. However, the cause of autoimmune diseases like psoriasis is unclear, although some evidence suggests that certain genetic pathways may influence the development of psoriasic dermatitis.
Several factors are implicated in the onset of psoriasis. The main contributors are disruptions to the KC barrier, the infiltration of activated immune cells, and the onset of the disease. The resulting psoriatic lesion consists of a confederacy of innate immunity-based genes and a defective terminal differentiation of epidermal cells. These inflammatory conditions are common, but there is no cure for the underlying cause of the disease.
In psoriasis, the immune system becomes overactive. Among its characteristics are abnormally high levels of cytokines, which stimulate inflammation in the skin and other organs. The disease is characterized by abnormally wide blood vessels and the accumulation of white blood cells. Keratinocytes multiply at an unusually rapid rate. These cells take about a month to mature and shed off.
The immune system and psoriasus are closely related. The body’s cells attack healthy skin, triggering inflammation and the proliferation of skin cells. The result is the characteristic red, painful plaque-like lesions. It is believed that the inflammatory response to such traumas triggers a cascade of inflammatory reactions in the skin, thereby causing new lesions. It is therefore necessary to understand how the immune system works to treat psoriasis.
As a result, the immune system plays a crucial role in psoriasis. Its inflammatory responses result in red plaques on the skin, which are caused by the proliferation of T cells. In addition to the immune response, a person’s skin also contains a variety of epidermal elements that are important for the condition. The underlying causes of psoriasis are unknown. The disease is considered an autoimmune disorder. There are several possible causes, including genetics, lifestyle.
There are many reasons why the immune system is important to psoriasis. The immune system is a vital part of the body that helps fight infection. When it functions well, it can protect the body from infections and other diseases. In some cases, the patient’s immune system is overactive, which can cause a psoriasis flare-up. If the underlying causes of psoriasis are genetic, they can affect a person’s immune system.
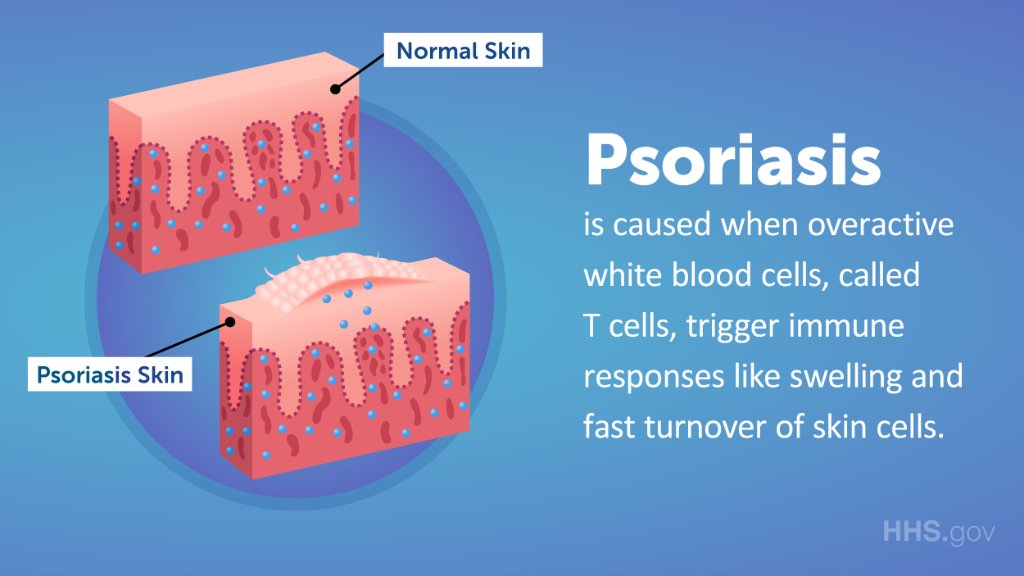
The immune system and psoriasis are closely related. Studies have shown that T cells from white blood cells infiltrate the skin and joints. The immune system controls the activity of these cells, and identifying the underlying causes is key to treating psoriasis. Inflammatory T cells are responsible for the development of psoriasis, and they also cause the disease.
The immune system and psoriasis are a complex relationship. However, the immune system and psoriatic dermatitis are closely related and may occur for the same reasons. The main factor that links psoriasis to the immune system is genetic. You can support and strengthen your immune system with a natural supplement Immutonus. Inflammatory bowel disease and diabetes are associated with a higher risk of developing psoriasis.
The immune system and psoriasis are linked. Inflammatory T cells are part of the immune system. This causes inflammation in the body. Its symptoms include dilated blood vessels, accumulation of white blood cells, and abnormal multiplication of keratinocytes, which are a type of skin cell. The resulting inflammatory process leads to the appearance of red plaques.
The immune system and psorias are associated with an overactive immune system. This means that the immune system attacks the body, causing the skin to swell and become painful. The disease is a chronic condition caused by overactive immune cells in the body. The treatment for psoriasis is not entirely clear yet, but it is a common cause of skin inflammation.
The immune system is the backbone of the immune system. There are several reactions in the body based on innate immunity. KCs and neutrophils are immune cells. Activated T cells are also believed to contribute to the development of psoriasis. Upper respiratory tract infections can cause psoriatic lesions, while secondary skin infection can be caused by a bacterial infection.