Understanding Your Heart’s Blood Flow
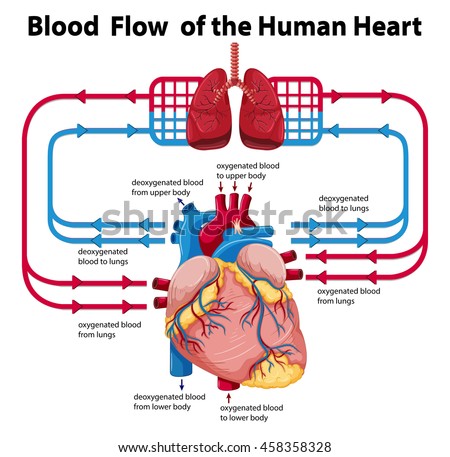
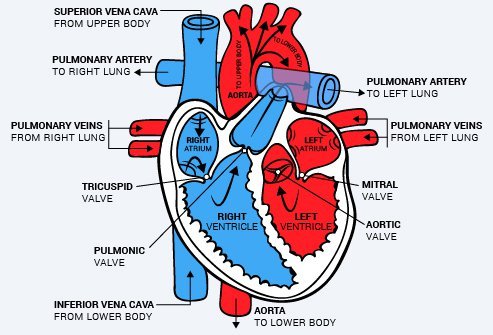
Arteries are any of the large arteries that, apart from one small artery, carry nutrition and oxygenated blood from the heart towards the various tissues of the body
The main exception is the pulmonary artery, which carries oxygen-depleted blood to the lungs in order to oxygenate and remove excess carbon dioxide from the blood (physiological ventilation). Other smaller arteries are common to all humans.
The most important function of arteries is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide and therefore they are very dense in relation to arterial walls. Because the arterioles carry oxygen-rich blood they have a wide diameter and so can accommodate a great deal of blood. In fact, the arteries are so wide that in the absence of hemoglobin, which is the substance that gives blood its red color, they are virtually indistinguishable from veins. These arteries carry blood from the internal organs to the bloodstream.
The walls of the arterioles are coated with a protein called lecithin, which acts as a buffer against the effects of blood coagulation. Blood that is clotting within the artery is not able to dissolve so this keeps it together and prevents it from sticking to surrounding tissue. As a result, this substance helps the arteries pass through blood clots without becoming damaged.
The arterioles are connected to all parts of your body and the muscles supporting them are attached to your diaphragm and your muscles. The pressure of blood within the arteries is greatest when there is a lack of exercise and it is greatest at rest when you are sitting and thus reducing the strain on these structures is important if you are going to reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease.
The arteries are important because they transport the oxygen-rich blood away from the interior of your body and to the parts where it is needed for energy production and the maintenance of high cholesterol levels. Therefore if the arteries become damaged or inflamed, they can cause permanent damage to other parts of your body such as the brain and the muscles and they can lead to cardiovascular problems. However, because arteries are so strong and because they are designed in such a way that they are able to cushion the flow of blood, it is unlikely that they will rupture without causing a serious injury.
If you already have a condition like atherosclerosis, you can be more likely to develop cardiovascular disease and aortic stenosis, also known as hardening of the arteries. This occurs when the walls of your artery become brittle and thin, usually this is accompanied by chest pain and you may notice your heart beating irregularly. If left untreated these symptoms can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Atherosclerosis is usually caused by an excessive accumulation of cholesterol in the walls of the arteries and can be controlled by certain medications that people with atherosclerosis take. However, if you are overweight, you can still develop atherosclerosis, so it is recommended that you control your weight. By controlling your weight with ยาลดน้ำหนัก, you also control the accumulation of fatty deposits in the artery wall, so there is less chance of it becoming too thick. Drinking plenty of water is also important.
If you have atherosclerosis and you suspect that you are experiencing heartburn, it is also recommended that you see your doctor immediately. Overweight people often develop plaque in their arteries. Plaque is made up of fat and cholesterol that build up between the walls of the arteries. Your doctor can advise you on which type of treatment is best for you.